In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, organizations face a mounting wave of cybersecurity challenges and threats. As cybercriminals grow increasingly sophisticated, businesses must prioritize the development of resilient cybersecurity programs that can effectively protect sensitive data, ensure uninterrupted operations, and safeguard their reputation.
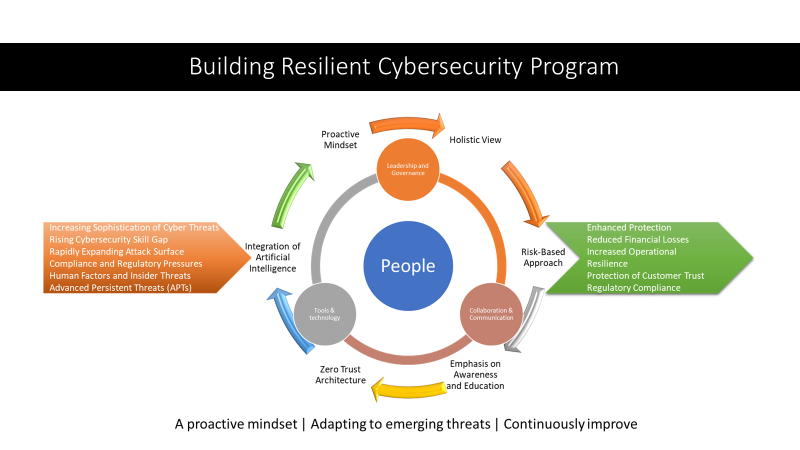
Current Challenges and Changing Landsacpe
Understanding the present challenges and the evolving nature of the landscape is paramount to designing a resilient cybersecurity program. Following are key challenges organisation are increasingly facing.
- Escalating Sophistication of Cyber Threats: Cybercriminals employ advanced techniques such as social engineering, ransomware, and zero-day exploits, necessitating constant vigilance and regular updates to defense systems. Organizations must stay ahead of these evolving threats by fortifying their security measures continually.
- Growing Cybersecurity Skill Gap: The demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals far surpasses the available talent pool. This shortage poses a significant challenge for organizations aiming to secure their networks and systems effectively. To address this issue, organizations must invest in comprehensive training and development programs to cultivate a competent cybersecurity workforce.
- Expanding Attack Surface: As organizations embrace digital transformation, their attack surfaces expand. Cloud environments, IoT devices, mobile apps, and remote work arrangements create new entry points for cyber attacks. Safeguarding these diverse and interconnected systems requires a proactive and all-encompassing approach to cybersecurity.
- Compliance and Regulatory Pressures: Regulatory frameworks and compliance requirements are in a constant state of flux. Organizations must navigate a complex web of data protection regulations, industry-specific compliance standards, and international privacy laws. Failing to comply with these regulations can result in severe financial and reputational consequences.
- Human Factors and Insider Threats: Human error remains one of the most significant vulnerabilities in cybersecurity. Employees may unintentionally fall victim to phishing attacks, mishandle sensitive data, or neglect security best practices. Additionally, both malicious and unintentional insider threats can pose substantial risks to an organization’s cybersecurity posture.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): APTs are highly sophisticated and stealthy cyber attacks that infiltrate organizations for extended periods, exfiltrating valuable data or sabotaging systems. These attacks often involve well-resourced threat actors with significant technical capabilities. Detecting and mitigating APTs requires advanced threat intelligence and constant monitoring.
To address these challenges and navigate the ever-changing landscape, organizations must adopt a proactive and adaptive approach to cybersecurity. This involves implementing robust security measures, staying informed about emerging threats, fostering a culture of security awareness, and harnessing advanced technologies like AI and machine learning to augment human capabilities.
Today’s Approach: Embracing the Evolving Landscape
The approach to cybersecurity has undergone a significant transformation in recent years, driven by the dynamic threat landscape and technological advancements. Several key differentiators set today’s approach apart from its predecessors:
- Proactive Mindset: Organizations have shifted from a reactive approach to a proactive mindset, prioritizing threat prevention over incident response. Continuous monitoring, threat intelligence, and proactive vulnerability management take precedence, enabling the detection and resolution of potential risks before they can be exploited.
- Holistic View: Cybersecurity is no longer confined to the realm of IT departments alone. It is now recognized as a strategic business function that necessitates collaboration across multiple stakeholders. Organizations involve senior management, business units, legal teams, HR, and employees at all levels to foster a culture of security and ensure a comprehensive approach.
- Risk-Based Approach: Organizations now adopt a risk-based approach, identifying and prioritizing risks based on their potential impact on business objectives. This approach allows for the allocation of resources and efforts where they are most needed, ensuring that cybersecurity measures align with the organization’s specific risk appetite.
- Emphasis on Awareness and Education: Organizations invest more in cybersecurity awareness and training programs for employees, recognizing that human error remains a significant vulnerability. These programs educate employees about cyber threats, safe practices, and their role in maintaining a secure environment.
- Zero Trust Architecture: Zero Trust has emerged as a prominent security framework that challenges traditional perimeter-based defenses. Organizations embrace the concept of assuming no trust, verifying every user and device before granting access to resources. This approach enhances security and mitigates risks associated with insider threats and compromised credentials.
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI technologies are increasingly employed to bolster cybersecurity efforts. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of data, detect anomalies, and identify potential threats with greater accuracy and speed. AI-powered tools enhance threat detection, incident response, and decision-making capabilities, providing organizations with a competitive edge against cyber threats.
These shifts in approach reflect the realization that cybersecurity is not merely a technical concern but a critical business imperative. By embracing a comprehensive, proactive, and risk-based approach while harnessing advanced technologies, organizations can better protect their assets, maintain operational resilience, and adapt to the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape.
Ensuring the Success of the Cybersecurity Program
To ensure the success of a cybersecurity program, it is essential to strike the right balance among various elements. The following pillars serve as the foundation and centerpiece for a thriving program:
- People: Engage and empower employees as key stakeholders in the cybersecurity program. Foster a culture of security awareness and accountability throughout the organization. Provide comprehensive training and awareness programs to educate employees about cybersecurity risks and best practices. Encourage a proactive approach to reporting and addressing potential threats and incidents.
- Leadership and Governance: Strong leadership and governance are vital for a successful cybersecurity program. Establish a dedicated cybersecurity team led by experienced professionals who can provide strategic direction, coordinate efforts, and oversee program implementation. Ensure that senior management actively supports the program and communicates its importance throughout the organization.
- Collaboration and Communication: Promote collaboration and open communication between different departments and stakeholders. Foster partnerships with IT, HR, legal, and other relevant teams to address cybersecurity challenges holistically. Encourage regular information sharing, threat intelligence exchanges, and collaborative incident response exercises.
- Technology and Tools: Leverage a range of technological solutions to enhance security. Implement firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, encryption technologies, secure remote access mechanisms, and robust endpoint protection. Advanced threat intelligence platforms and security analytics tools can help identify and respond to emerging threats effectively.
By integrating people, technology, and tools with a clear mandate, organizations can enhance the effectiveness and resilience of their cybersecurity programs. Remember, cybersecurity is an ongoing journey that requires commitment, collaboration, and a willingness to evolve with the changing landscape.
The Rewards of a Resilient Cybersecurity Program
A well-executed cybersecurity program yields several significant outcomes for an organization:
- Enhanced Protection: A robust cybersecurity program significantly strengthens an organization’s defenses against cyber threats. It minimizes the risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, and other security incidents, safeguarding sensitive information and preserving the organization’s reputation.
- Reduced Financial Losses: Effective cybersecurity measures help mitigate financial losses associated with security breaches. By preventing or minimizing the impact of cyber incidents, organizations can avoid costly legal battles, regulatory fines, customer compensation, and damage to their brand value.
- Increased Operational Resilience: A resilient cybersecurity program enhances the resilience of business operations. It ensures the continuous availability and reliability of critical systems and data, minimizing downtime and disruptions caused by cyber attacks.
- Protection of Customer Trust: With growing concerns about data privacy, a successful cybersecurity program reassures customers that their personal information is secure. By prioritizing data protection, organizations can build and maintain trust with their customers, leading to stronger relationships and loyalty.
- Regulatory Compliance: A well-designed cybersecurity program facilitates compliance with industry regulations and data protection laws. By aligning security practices with regulatory requirements, organizations can avoid penalties, legal liabilities, and reputational damage.
By prioritizing cybersecurity and embracing a proactive, holistic approach, organizations can navigate the ever-changing landscape with confidence, secure their digital assets, and foster resilience in the face of evolving cyber threats.