Project management is the application of processes, methods, skills, knowledge, and experience to the achievement of specific project objectives. It is a critical function for any organization that wants to successfully deliver projects on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards.
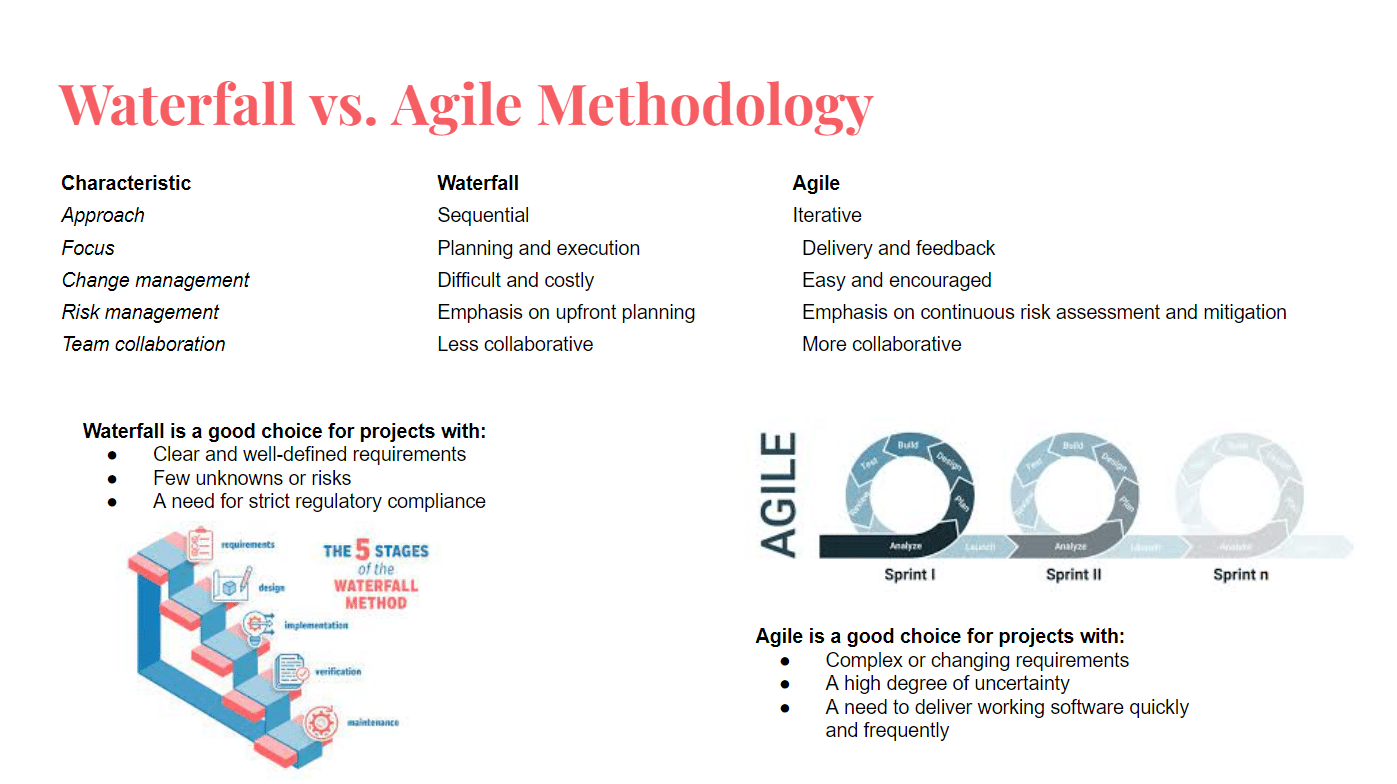
There are two main project management methodologies: waterfall vs. agile. Both have their own strengths and weaknesses, and the best approach for a particular project will depend on a number of factors, such as the project’s complexity, scope, and uncertainty.
Which Methodology is Right for You?
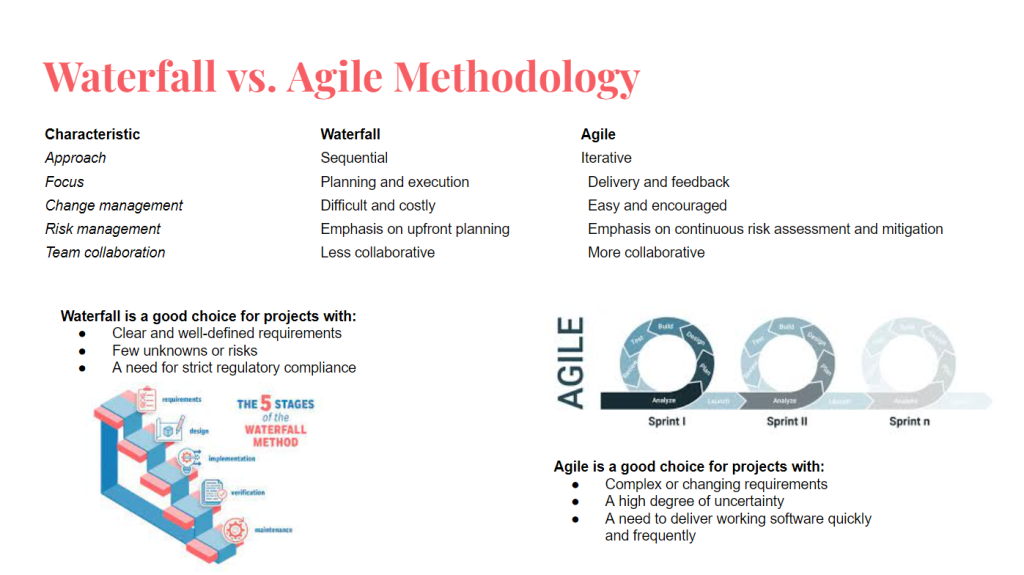
The best project management methodology for you will depend on a number of factors, including the project’s complexity, scope, and uncertainty. If you have a well-defined project with clear requirements and few unknowns, then the waterfall methodology may be a good fit. However, if you have a complex project with changing requirements, then the agile methodology may be a better choice.
It is important to note that waterfall and agile are not mutually exclusive. Many organizations use a hybrid approach that combines elements of both methodologies. For example, a team may use a waterfall approach for the initial planning and design phases of a project, and then switch to an agile approach for the development and deployment phases.
Ultimately, the best way to choose the right project management methodology is to carefully consider the specific needs of your project and team.
The Key Differences
| Waterfall | Agile | |
|---|---|---|
| Project Phases | The Waterfall methodology divides the project into distinct, sequential phases. Each phase must be completed before moving on to the next. Phases include requirements gathering, design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance. | Agile, on the other hand, breaks the project into smaller, iterative cycles called sprints. These sprints allow for continuous development and testing. There is no need to wait for one phase to complete before initiating the next. Agile emphasizes flexibility and adaptability throughout the project. |
| Flexibility | Waterfall is a rigid approach with limited flexibility for changes once a phase begins. If there are significant changes or errors discovered later in the project, it can be costly and time-consuming to rectify. | Agile embraces change and encourages collaboration with stakeholders. Changes can be easily accommodated during the project’s lifecycle, resulting in a more adaptable approach. |
| Client Involvement | Client involvement is usually limited to the beginning and end of the project. Clients provide requirements at the start and review the final product at the end. | Agile promotes ongoing collaboration with clients throughout the project. They have the opportunity to review and provide feedback after each sprint, ensuring that the project aligns with their evolving needs. |
| Risk Management | Risks are identified and addressed at the beginning of the project. This can lead to unforeseen risks emerging later in the project that may be difficult to mitigate. | Agile continuously identifies and addresses risks throughout the project. This proactive approach allows for the timely mitigation of potential issues. |
| Project Visibility | Project progress is typically less visible until the later stages when substantial work has been completed. | Agile provides greater project visibility from the early stages, with frequent demonstrations of working components, enhancing transparency for stakeholders. |
| Testing and Quality Assurance | Testing is usually conducted at the end of the project. This can lead to a higher probability of identifying defects and issues late in the project. | Agile includes testing throughout the project, ensuring that issues are identified and resolved promptly, resulting in a higher-quality end product. |