In recent years, the financial sector has witnessed the emergence of various innovative practices aimed at promoting sustainability and environmental responsibility. Among these, Regenerative Finance (ReFi) stands out as a paradigm-shifting approach that extends beyond the conventional boundaries of sustainable finance, and decentralized finance (DeFi). This blog post delves into the essence of Regenerative Finance, its unique business case, real-world examples, and how it differentiates itself from related concepts in the finance sector.
Understanding Regenerative Finance
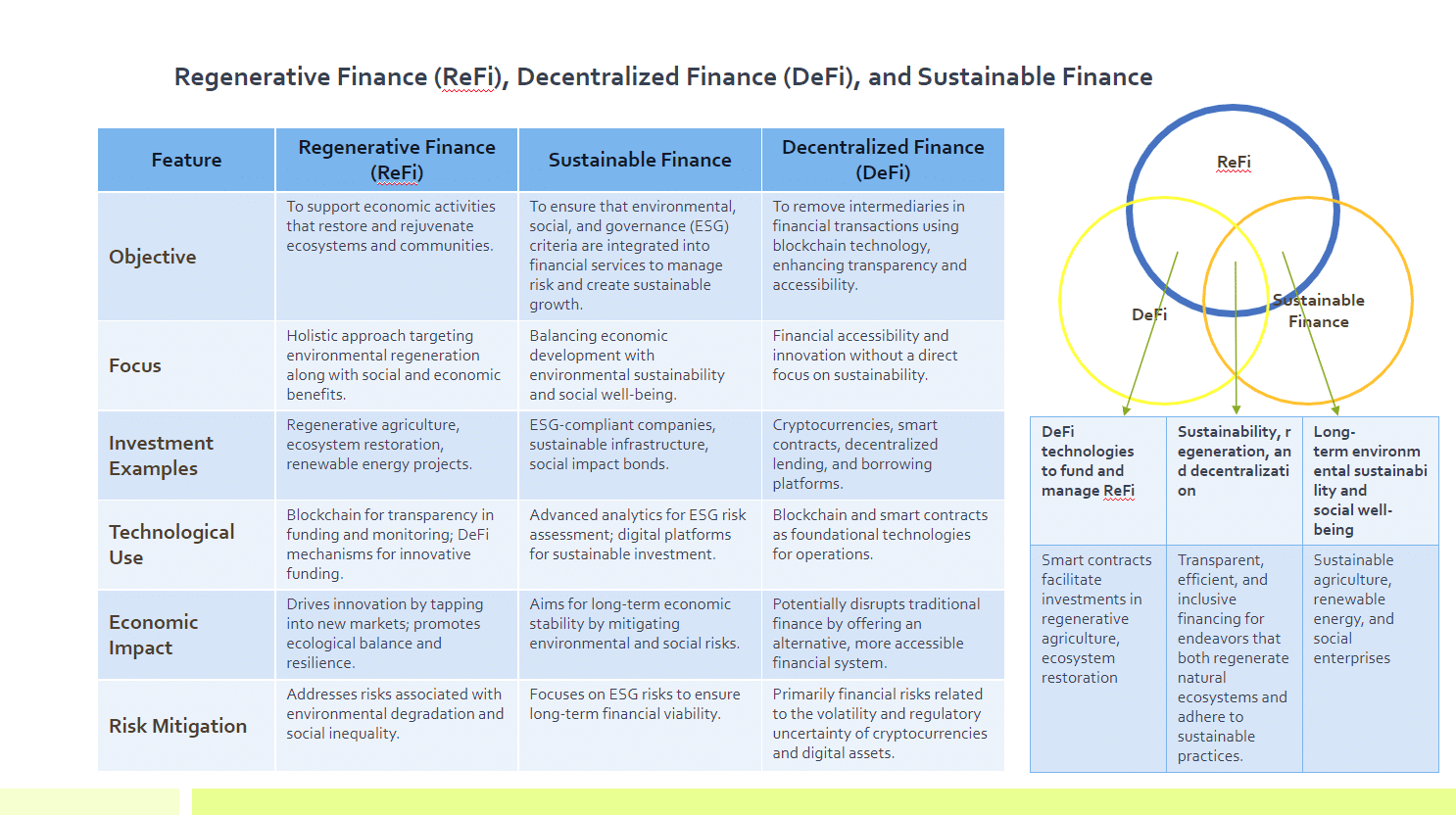
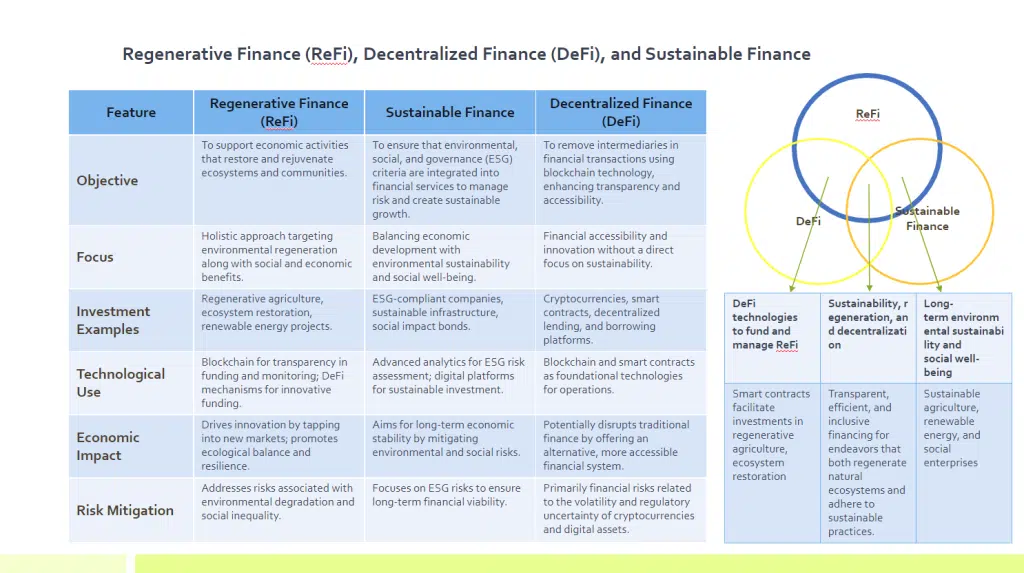
Regenerative Finance is an innovative financial model that aims to support economic activities which restore and rejuvenate ecosystems, communities, and the biosphere at large, rather than merely minimizing harm. It embodies a holistic approach, prioritizing investments in projects and businesses that contribute to the health of the planet and its inhabitants. ReFi is not just about funding green initiatives; it’s about creating a financial system that actively contributes to the regeneration of natural and social systems.
The Business Case for Regenerative Finance
The business case for Regenerative Finance is compelling. It offers a path to long-term sustainability by investing in projects that have a positive impact on the environment and society. This approach helps mitigate risks associated with environmental degradation, such as climate change and resource scarcity, which can have profound economic implications. Moreover, by focusing on regeneration, companies and investors can tap into new markets and opportunities for innovation, driving economic growth while promoting ecological balance.
Examples of Regenerative Finance in Action
One notable example of Regenerative Finance is the investment in regenerative agriculture practices. These practices, which include crop rotation, agroforestry, and organic farming, not only reduce carbon footprint but also enhance soil health, biodiversity, and water conservation. By funding such initiatives, ReFi supports sustainable food systems while offering financial returns through increased crop yields and resilience to climate change.
Another example is the restoration of natural ecosystems through reforestation projects and wetlands restoration. These projects not only sequester carbon but also protect biodiversity and support local communities. Investments in renewable energy projects, like solar and wind farms, also fall under the umbrella of Regenerative Finance, contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and the promotion of energy independence.
The Role of Technology in Regenerative Finance
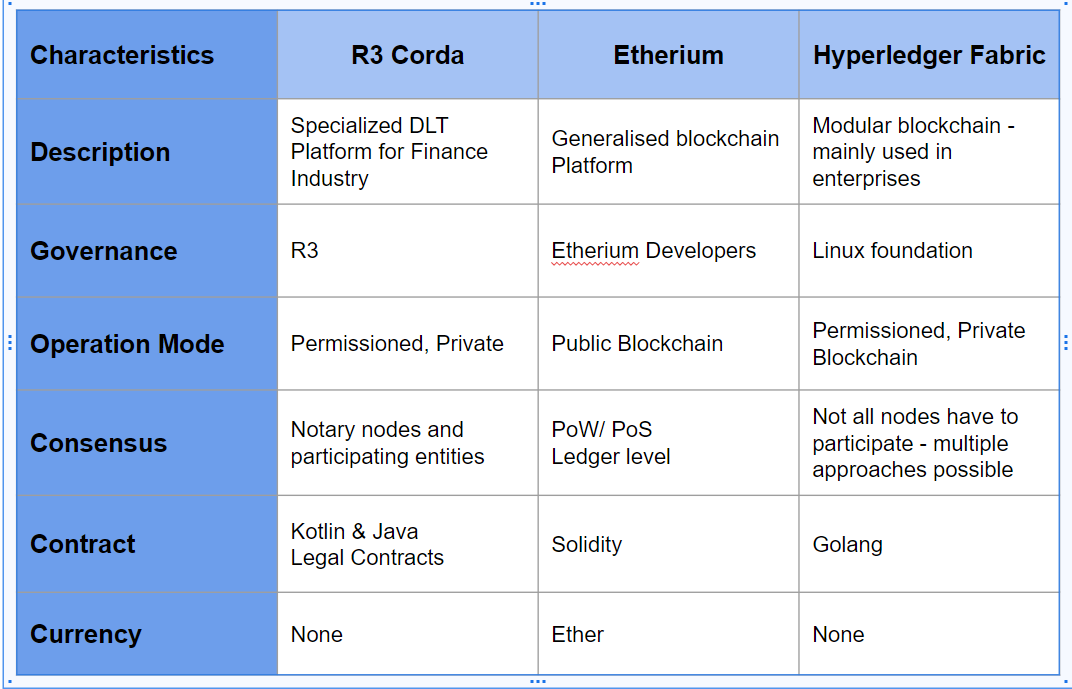
Technology plays a pivotal role in Regenerative Finance, especially through the use of blockchain and DeFi mechanisms. Blockchain technology facilitates transparency, traceability, and efficiency in financial transactions, making it easier to fund and monitor regenerative projects. Smart contracts and tokens can incentivize sustainable practices and provide new forms of funding for regenerative projects.
Conclusion
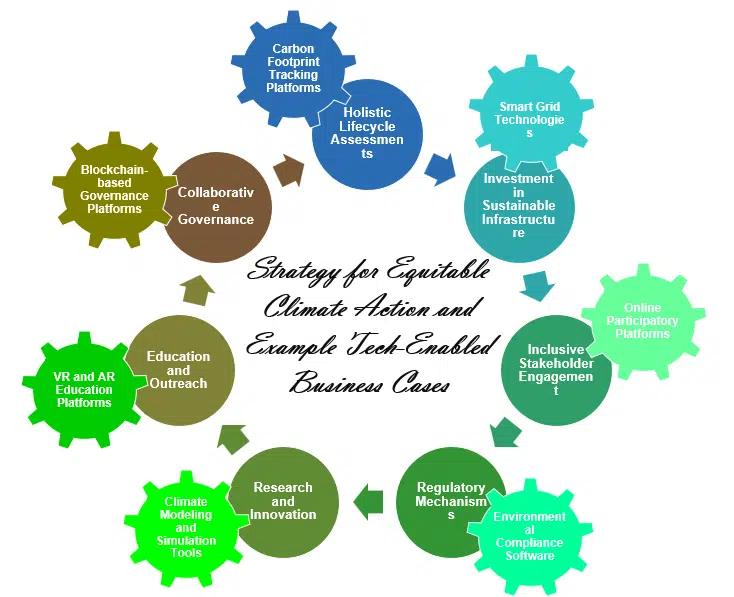
Regenerative Finance represents a significant shift in how we approach investment and economic growth. By prioritizing the regeneration of natural and social systems, ReFi not only addresses the urgent challenges of environmental degradation and social inequality but also opens up new avenues for sustainable economic development. As more businesses and investors recognize the value of Regenerative Finance, we can expect to see a growing number of innovative projects aimed at restoring our planet and building a more equitable and sustainable future for all.